
There is no getting away from it—the only way to burn fat and lose weight is with an energy deficit (1). This means you either need to consume fewer kilocalories than you burn or burn more than you eat. Invariably, creating this all-important energy deficit boils down to eating less and moving more.
Sure, you could rely on diet alone or try to exercise yourself slimmer, but studies suggest that, for most people, the combination of diet and exercise is usually more effective (2).
I’m a veteran personal trainer with more than three decades of experience, and a significant proportion of my clients come to me for weight loss advice. In return, I help them plan and execute their workouts while teaching them the ins and outs of healthy eating.
Many assume that their new diet is going to be boring, repetitive, and bland because that’s been their experience with other weight loss eating plans. But that’s not how I roll! Instead, I want their meals to be as satisfying and enjoyable as possible.
To achieve this, I always recommend that my weight loss clients include plenty of herbs and spices in their meals. Despite being kilocalorie-free, these ingredients add a whole new layer of taste to even the most basic ingredients.
But herbs and spices don’t just add flavor—some can even enhance fat burning.
Level Up Your Fitness: Join our 💪 strong community in Fitness Volt Newsletter. Get daily inspiration, expert-backed workouts, nutrition tips, the latest in strength sports, and the support you need to reach your goals. Subscribe for free!
Please wait…
In this article, I share my three favorite (and scientifically proven) metabolism-boosting spices and provide some ideas for how to incorporate them into your diet.

Before I reveal the three best metabolism-boosting thermogenic spices, let’s take a moment to clarify what metabolism and thermogenesis actually are. This will help you make better sense of how these substances work, and what they can do for you.
Metabolism
Metabolism is the word used to describe all the complex chemical reactions that occur within your body. In the simplest terms, it’s how your body uses the food you eat and converts it into energy.
Your metabolism never rests, and even while you sleep it’s busy maintaining organ function, circulating blood, controlling temperature, repairing cells, and so much more. This is known as your basal metabolic rate (BMR), and it accounts for the largest portion of your daily energy expenditure.
Your remaining energy expenditure comes from powering physical activity, both purposeful exercise and incidental movements, and the thermic effect of food. That’s because eating, digesting, transporting, and eliminating food also uses energy.
Your metabolic rate—the amount of energy used for all these processes—is typically measured in kilocalories or kilojoules, which are also measures of heat expenditure.
Just like turning up the thermostat in your home uses more fuel, raising your metabolic rate increases the number of kilocalories you burn each day. Consequently, if your goal is to lose weight and fat as quickly and easily as possible, the last thing you want is a sluggish metabolism. Rather, you want to raise your metabolic rate.
Related: BMR Calculator: Find Your Basal Metabolic Rate
Thermogenesis
Thermogenesis refers to heat production in your body. Like many chemical reactions, all the processes responsible for keeping you alive generate heat, which is why the energy value of food is expressed as a measure of heat.
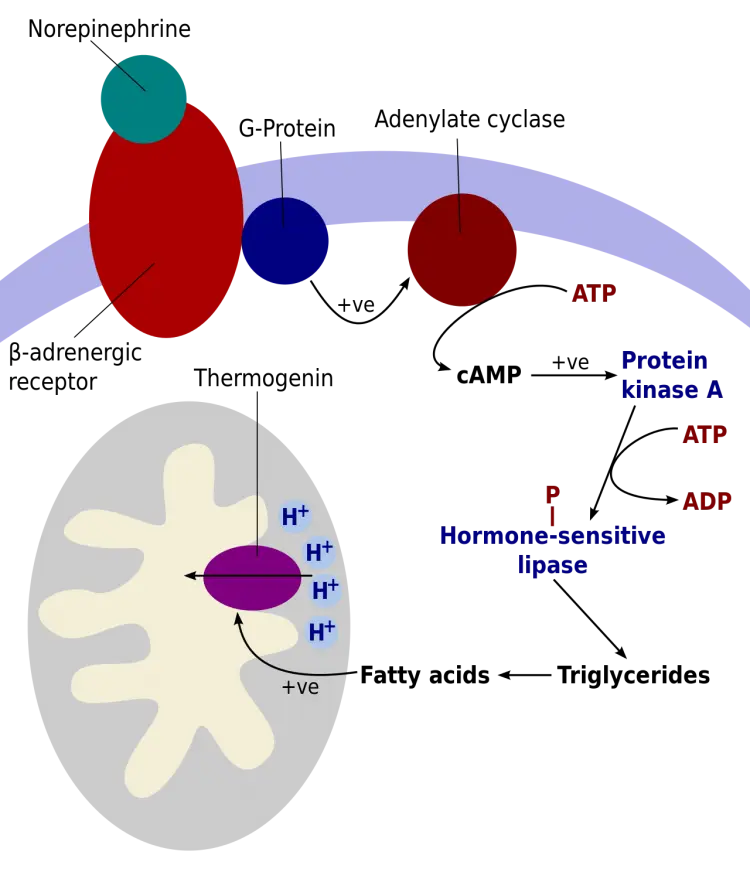

There are a few different types of thermogenesis:
- Basal thermogenesis – the heat produced by your body at rest
- Exercise-induced thermogenesis – the heat generated during physical activity
- Non-exercise activity thermogenesis (NEAT) – the energy used for everything else, like fidgeting or walking
- Diet-induced thermogenesis – the rise in metabolism after eating, also called the thermic effect of food
- Adaptive thermogenesis – the effect of certain foods and ingredients—including spices—that slightly increase your metabolic rate.
Related: Fitness Through Fidgeting: How I Burned 500 Extra Calories a Day Without ‘Exercising’
What Are Thermogenic Spices?
Thermogenic spices increase energy expenditure by stimulating heat production. They contain compounds that temporarily raise your metabolic rate by increasing heat output and energy use.
Have you ever felt hot after eating a fiery meal? That’s the thermogenic spices in action.
However, while the effects are definitely noticeable and sound impressive, it’s important to keep things in perspective. That’s because, while thermogenic spices are proven to increase your metabolism (3), their effect is still very mild.
What Thermogenic Spices Can and Can’t Do

Thermogenic spices can:
- Slightly increase energy expenditure
- Support fat oxidation
- Make meals more enjoyable so your diet is easier to stick to
- Provide other health benefits, like anti-inflammatory or antioxidant effects
Thermogenic spices can’t:
- Replace the need for a calorie deficit
- Dramatically accelerate fat loss on their own
- Compensate for poor dietary habits or inactivity
Think of thermogenic spices as support tools—they give you a slight edge when used alongside a solid nutrition and training plan. They’re not shortcuts, but they can make your meals tastier, and your fat loss plan a little more effective.
Don’t let that put you off, though as, in the battle for faster, easier weight loss and fat burning, every advantage counts!
The Three Best Thermogenic Spices for Fat Loss
While all warming spices have the potential to elevate your metabolism, the following three are arguably the best. However, only add them in small amounts because, if you are unaccustomed to their heat, using too much could make your meals inedible and even cause digestive issues.
1. Black Pepper

Black pepper is a common ingredient in many meals. It’s also a popular table condiment. Freshly ground black pepper is a major taste enhancer, and lots of people add it to food. It’s also a proven thermogenic spice.
The active compound in black pepper is a substance called piperine, which is responsible for both black pepper’s flavor and heat. In animal studies, black pepper consumption has been shown to increase metabolism and weight loss, even without a significant energy deficit (4).
Uses:
Level Up Your Fitness: Join our 💪 strong community in Fitness Volt Newsletter. Get daily inspiration, expert-backed workouts, nutrition tips, the latest in strength sports, and the support you need to reach your goals. Subscribe for free!
Please wait…
The best way to harness the thermogenic effect of piperine is to freshly grind and sprinkle black pepper on your meals. It goes great with most types of food and even works well on some fruits, such as watermelon and strawberries. Start with a small amount and then increase as you develop a tolerance to the flavor and heat.
2. Cayenne Pepper
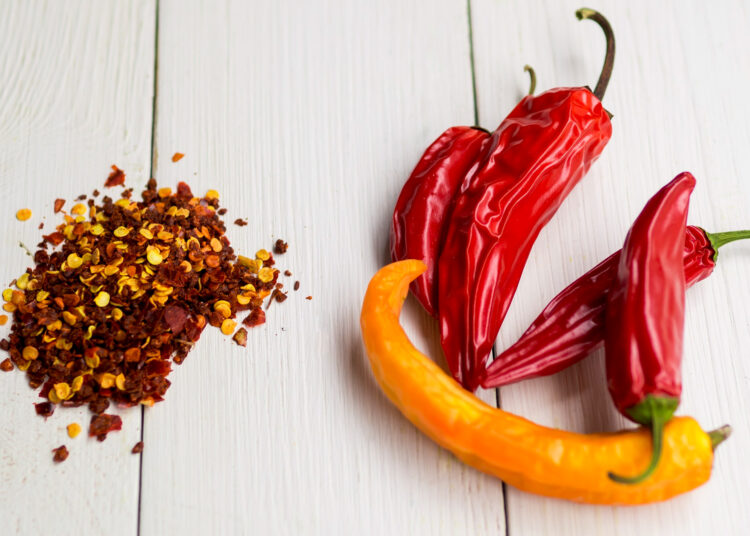

Cayenne is a type of pungent chili pepper used in many cuisines. It contains the compound capsaicin, which provides cayenne with its signature heat and flavor. Capsaicin is linked to numerous health benefits, not least elevated metabolism and fat burning.
In studies, capsaicin has been shown to increase post-consumption metabolic rate while enhancing fat metabolism (5). Evidence also suggests that cayenne may act as a mild appetite suppressant (6).
Uses:
Cayenne pepper is a common ingredient in many types of food. Try replacing your regular breakfast, lunch, or dinner with something that contains cayenne pepper, for example:
- Mexican/Tex-Mex: Chili con carne, tacos, enchiladas, spicy salsas
- Cajun/Creole: Jambalaya, gumbo, blackened fish or chicken
- Indian: Vindaloo, madras curry, spiced lentils (dal)
- Caribbean: Jerk chicken or pork, pepper sauces
- Thai/Southeast Asian: Tom yum soup, spicy stir-fries, curry pastes
- Middle Eastern/North African: Harissa, shakshuka, tagines
Alternatively, experiment with adding cayenne to your usual meals – it’s a great addition to things like eggs, meat, fish, and vegetables. However, a little goes a long way, so start with a small serving, e.g. ¼ teaspoon, to see how you tolerate the heat this pungent spice contains.
3. Ginger
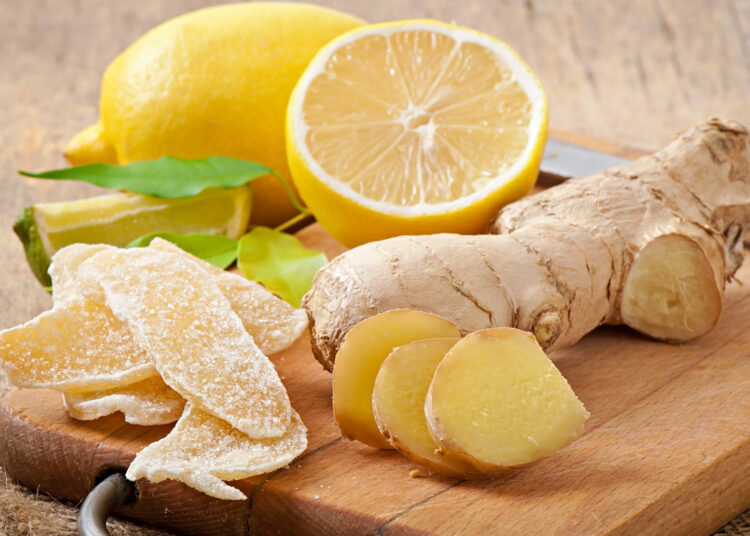

Ginger is a versatile spice that can be used in sweet and savory dishes as well as beverages. While you can get powdered ginger, the fresh root—available in most grocery stores—is arguably the most thermogenic and tasty option.
Studies show that ginger has a potent metabolism-boosting effect and its proven benefits include a reduction in body weight, fat mass, and body fat percentage (7). In addition, ginger is thought to aid digestion and is also often better tolerated than hotter spices like cayenne and chili.
Uses:
Fresh ginger root is very warming and tasty, and it works well in curries and other spicy dishes. However, I’ve also found that it’s perfect for making a metabolism-boosting drink.
Using the back of a knife or a spoon, scrape the skin off a thumb-sized piece of ginger. Cut into thin slices and add to a cup of boiling water and your favorite herbal tea. Allow to steep for 5-10 minutes and then enjoy a warming, relaxing alternative to regular tea or coffee.
Honorable Mentions
While black pepper, cayenne, and ginger are among the best metabolism-boosting spices, there are several others that are worth adding to your meals. These include:
- Turmeric – contains curcumin, which has mild thermogenic properties and may also help reduce inflammation.
- Cinnamon – helps regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity, indirectly supporting fat loss.
- Mustard Seeds – contain compounds that may increase metabolic rate and energy expenditure.
- Cardamom – traditionally used to aid digestion and may have mild thermogenic effects.
- Cloves – rich in antioxidants and may support digestion and fat oxidation.
- Cumin – studies suggest it may help reduce body weight and waist circumference (8).

Closing Thoughts
Eating for weight loss doesn’t have to mean dull, tasteless meals. In fact, adding the right spices can transform your diet—making it more enjoyable and slightly more effective for fat loss by boosting your metabolism.
While thermogenic spices don’t replace the need for an energy deficit or a consistent exercise program, they can give your metabolism a subtle nudge in the right direction. More importantly, they can help make your diet easier to stick to by making your meals more satisfying.
So, don’t be afraid to experiment. Embrace bold flavors, try new cuisines, and turn every meal into something you actually look forward to eating. Your tastebuds—and your waistline—will thank you.
Ready to spice up your fat loss journey? Pick one of these potent seasonings and add it to your next meal. Small changes really can lead to big results.
Related: The Walk & Tone Summer Program: How to Turn Your Daily Stroll into a Full-Body Sculptor
References
Fitness Volt is committed to providing our readers with science-based information. We use only credible and peer-reviewed sources to support the information we share in our articles.
1 – Strasser B, Spreitzer A, Haber P. Fat loss depends on energy deficit only, independently of the method for weight loss. Ann Nutr Metab. 2007;51(5):428-32. doi: 10.1159/000111162. Epub 2007 Nov 20. PMID: 18025815.
2 – Wu T, Gao X, Chen M, van Dam RM. Long-term effectiveness of diet-plus-exercise interventions vs. diet-only interventions for weight loss: a meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2009 May;10(3):313-23. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-789X.2008.00547.x. Epub 2009 Jan 19. PMID: 19175510.
3 – Ludy MJ, Moore GE, Mattes RD. The effects of capsaicin and capsiate on energy balance: critical review and meta-analyses of studies in humans. Chem Senses. 2012 Feb;37(2):103-21. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjr100. Epub 2011 Oct 29. PMID: 22038945; PMCID: PMC3257466.
4 – Shah SS, Shah GB, Singh SD, Gohil PV, Chauhan K, Shah KA, Chorawala M. Effect of piperine in the regulation of obesity-induced dyslipidemia in high-fat diet rats. Indian J Pharmacol. 2011 May;43(3):296-9. doi: 10.4103/0253-7613.81516. PMID: 21713094; PMCID: PMC3113382.
5 – Zheng J, Zheng S, Feng Q, Zhang Q, Xiao X. Dietary capsaicin and its anti-obesity potency: from mechanism to clinical implications. Biosci Rep. 2017 May 11;37(3):BSR20170286. doi: 10.1042/BSR20170286. PMID: 28424369; PMCID: PMC5426284.
6 – Janssens PL, Hursel R, Westerterp-Plantenga MS. Capsaicin increases sensation of fullness in energy balance and decreases desire to eat after dinner in negative energy balance. Appetite. 2014 Jun;77:44-9. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2014.02.018. Epub 2014 Mar 12. PMID: 24630935.
7 – afieipour N, Gharbi N, Rahimi H, Kohansal A, Sadeghi-Dehsahraei H, Fadaei M, et al. Ginger intervention on body weight and body composition in adults: a GRADE-assessed systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of 27 randomized controlled trials. Nutr Rev. 2024;82(12):1651–65. doi:10.1093/nutrit/nuad149
8 – Zare R, Heshmati F, Fallahzadeh H, Nadjarzadeh A. Effect of cumin powder on body composition and lipid profile in overweight and obese women. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2014 Nov;20(4):297-301. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2014.10.001. Epub 2014 Oct 13. PMID: 25456022.







